Wiring Batteries In Parallel
Wiring batteries in parallel means connecting the positive terminals of multiple batteries together and the negative terminals together, effectively increasing the total capacity of the battery bank. This results in a higher overall current capacity while maintaining the same voltage as a single battery.
In a parallel connection, the positive terminals are connected to each other, and the negative terminals are connected to each other. This configuration allows for the combined capacity of the batteries to be utilized, providing a longer run time and increased current output.
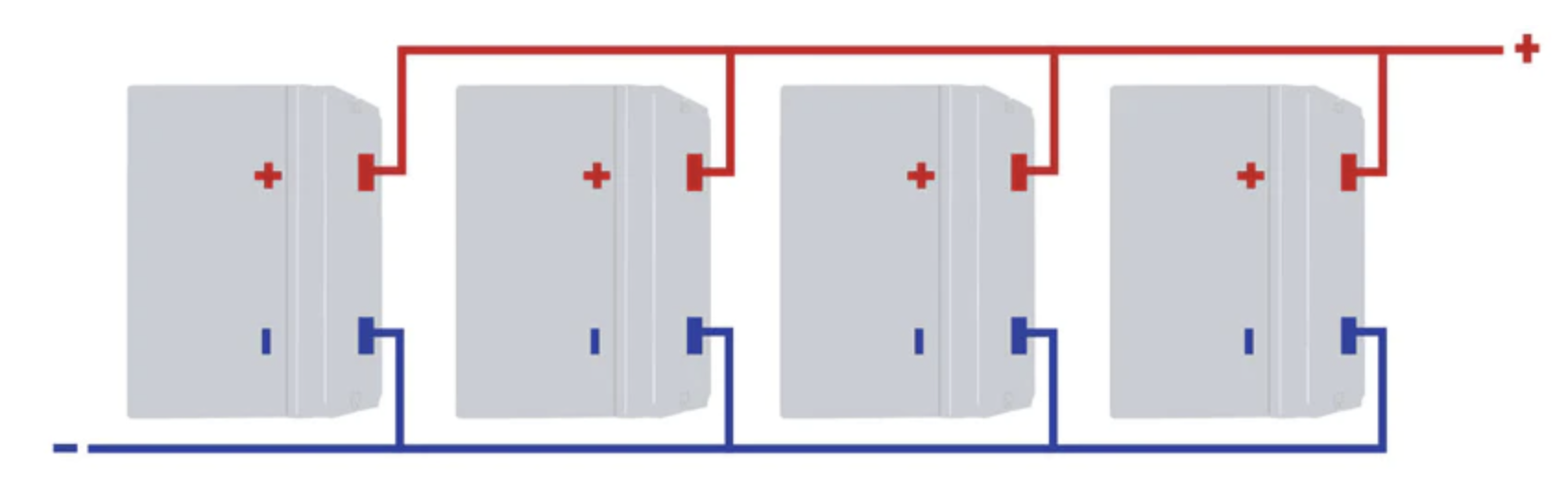
For example, if two batteries with a capacity of 1000mAh each are connected in parallel, the resulting battery bank will have a capacity of 2000mAh. This means that it can provide twice the run time compared to a single battery of 1000mAh.
Wiring batteries in parallel has several advantages, including:
- Increased capacity: Parallel connection increases the overall capacity of the battery bank, allowing for longer run times.
- Lower overall cost: Wiring batteries in parallel requires fewer batteries compared to a series connection, resulting in a lower overall cost.
- Higher current output: Parallel connection enhances the overall current capacity of the battery bank, making it suitable for applications that require high current draw.
However, there are a few considerations when wiring batteries in parallel:
- Balancing: It is important to ensure that all the batteries in the parallel connection have similar capacities and states of charge to prevent imbalances and potential damage to the batteries.
- Charging: Charging a parallel-connected battery bank may require a charger with a higher current output to avoid extended charging times.
*Careful consideration of the specific requirements and limitations of the application is essential before deciding to wire batteries in parallel.
