Wiring Batteries In Series
Wiring batteries in series means connecting the positive terminal of one battery to the negative terminal of another battery, and so on, to increase the total voltage of the battery bank.
In a series connection, the total voltage is the sum of the individual battery voltages. The positive terminal of the first battery becomes the positive output terminal, and the negative terminal of the last battery becomes the negative output terminal of the series-connected batteries.
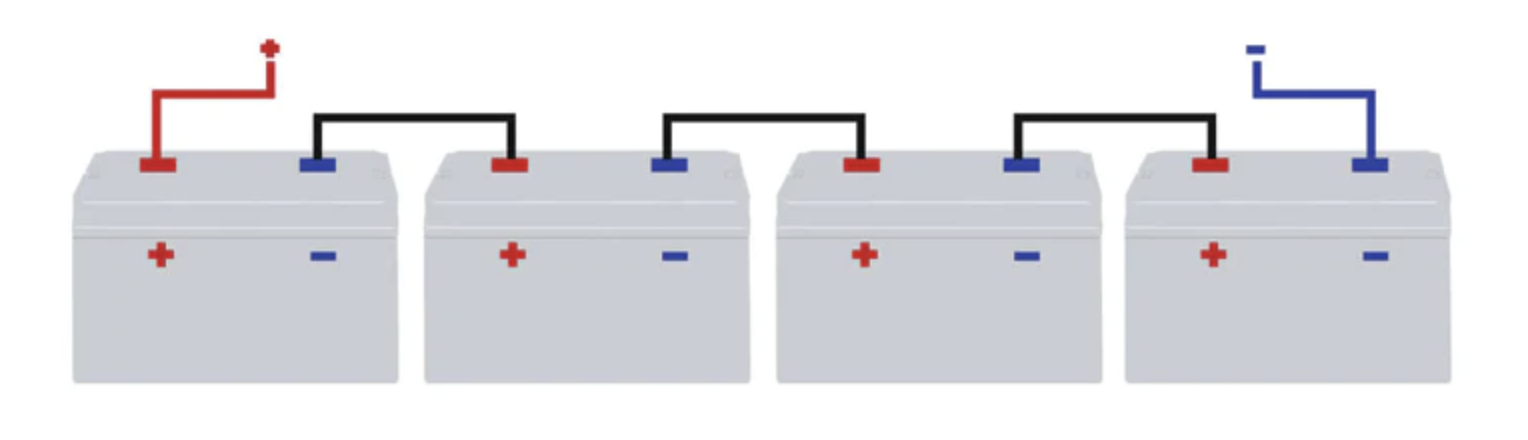
For example, if you have two 12V batteries and wire them in series, the total voltage output would be 24V (12V + 12V). This is commonly used in applications where higher voltage is required, such as in electric vehicles or solar power systems.
However, it's crucial to ensure that the batteries being connected in series have the same voltage rating and capacity to prevent imbalances and potential damage.
Reported Pros to Wiring Your Batteries in Series
- Increased voltage: Wiring batteries in series increases the total voltage output, which can be advantageous in applications that require higher voltage levels.
- Longer run time: By increasing the voltage, the battery bank can provide power for a longer duration, making it suitable for devices or systems that need extended run times.
- Efficient charging: When charging a series-connected battery bank, the higher voltage allows for more efficient charging as it reduces the charging time.
Reported Cons of Wiring Your Batteries in Series
- Increased risk of imbalance: If the batteries in a series connection have different capacities or states of charge, they can become imbalanced. Imbalanced batteries can lead to reduced overall performance, decreased lifespan, and potential damage to the batteries.
- Higher cost: Wiring batteries in series requires more batteries compared to a parallel connection, which can increase the overall cost of the battery bank.
- Limited current capacity: While the voltage increases, the overall current capacity remains the same as that of an individual battery. This means that the series-connected battery bank may not be suitable for applications that require high current draw.
*It is important to carefully consider the specific requirements and limitations of the application before deciding to wire batteries in series.
